Optimization of the active component grinding process and hydrophobization of the obtained powder fire extinguisher Technical paper
Main Article Content
Abstract
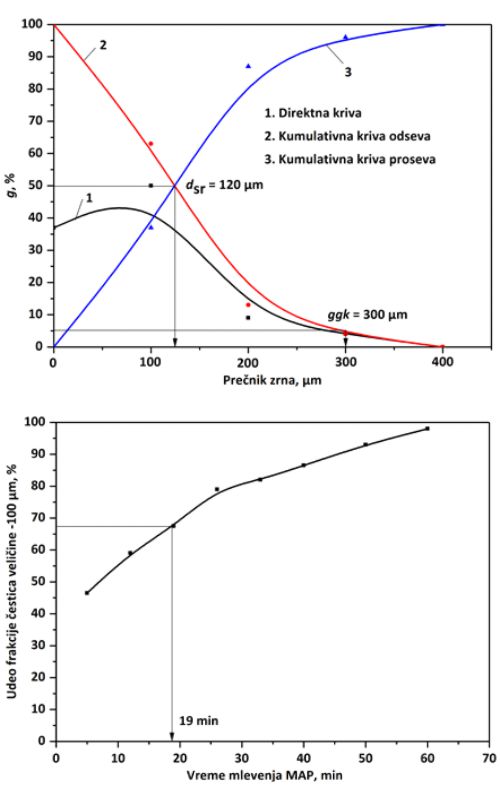
This work presents a grinding process of monoammonium phosphate (MAP) as an active component in a powder fire extinguisher (PFE). The aim was to determine the grinding time for reaching the optimal particle size of MAP necessary for permanent fire extinguishing. MAP grinding was performed by using a laboratory ceramic ball mill and a vibrating cup mill. The grinding process was controlled by sieving using a 100 µm sieve at precisely defined time intervals. The efficiency of a PFE depends on the share of the -100 µm fraction of the active component, which has to exceed 60 %. The optimal grain size with 64 % of fraction of particle size -100 µm was obtained after 33 min of grinding of ≈3000 µm mm grain size MAP by using a ball mill (single-stage grinding). In two-stage process, by grinding the same initial MAP sample (≈3000 µm) in the vibro mill for 10 min, powder with the upper limit grain size of 300 µm and the mean grain diameter of 120 µm was obtained. This sample with a reduced size was further ground in the ceramic ball mill yielding 67.5 % of the fraction of particle size -100 µm after 19 min. The total time of the two-stage grinding process was 29 min. By analyzing the grinding time of MAP required to get the lowest required share of the fraction of particle size -100 µm that provides the effectiveness of formed PFE it can be concluded that 64 % of this fraction was obtained after 33 min of single-stage grinding, while only after 26 min in the two-stage process. Thus, the grinding time was reduced by 7 min indicating certain energy savings. Stability and hydrophobicity of the obtained PFE were achieved by coating with magnesium stearate (MgSt) at the content of 2 % in a ball mill for 15 min. The coating was confirmed by the standardized procedure for verification of PFE hydrophobic properties in contact with water drops. To obtained PFE had component mass ratios of MAP:AS:CC:QS:MgSt=55:20:18:5:2 (AS-ammonium sulfate; CC-calcium carbonate, QS-quartz sand) and was further characterized by chemical and granulometric analyses. The fire extinguishing efficiency of the PFE was tested in controlled conditions, whereby fires were initiated by burning solid materials and flammable liquids. In both cases, immediate elimination of flames was achieved, thus proving the efficiency of the PFE obtained in this work for practical applications..
Article Details
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors grant to the Publisher the following rights to the manuscript, including any supplemental material, and any parts, extracts or elements thereof:
- the right to reproduce and distribute the Manuscript in printed form, including print-on-demand;
- the right to produce prepublications, reprints, and special editions of the Manuscript;
- the right to translate the Manuscript into other languages;
- the right to reproduce the Manuscript using photomechanical or similar means including, but not limited to photocopy, and the right to distribute these reproductions;
- the right to reproduce and distribute the Manuscript electronically or optically on any and all data carriers or storage media – especially in machine readable/digitalized form on data carriers such as hard drive, CD-Rom, DVD, Blu-ray Disc (BD), Mini-Disk, data tape – and the right to reproduce and distribute the Article via these data carriers;
- the right to store the Manuscript in databases, including online databases, and the right of transmission of the Manuscript in all technical systems and modes;
- the right to make the Manuscript available to the public or to closed user groups on individual demand, for use on monitors or other readers (including e-books), and in printable form for the user, either via the internet, other online services, or via internal or external networks.
How to Cite
References
Zhao J, Yin Z, Shahid UM, Xing H, Cheng X, Fu Y, Lu S. Superhydrophobic and oleophobic ultra-fine dry chemical agent with higher chemical activity and longer fire-protection. J Hazard Mater. 2019; 380: 120625.
Huang Ch, Chen X, Yuan B, Zhang H, Shang, Sh, Zhao Q, Dai H, He S, Zhang Y, Niu Y. Insight into suppression performance and mechanisms of ultrafine powders on wood dust deflagration under equivalent concentration. J Hazard Mater. 2020; 394: 122584.
Xiaomin N, Chow WK. Fundamental suppression chemistry of clean fire suppressing agents: A Review. J Appl Fire Sci. 2011; 21(3): 223-251.
Ewing CT, Faith FR, Huges JT, Carhart HW. Flame extinguishment properties of dry chemicals: Extinction concentrations for small diffusion pan fires. Fire Technol. 1989; 25: 134-149.
Zhao G, Xu G, Jin Sh, Zhang Q, Liu Zh. Fire-Extinguishing efficiency of superfine powders under different Injection pressures. Int J Chem Eng. 2019; Article 2474370.
Su Ch, Chen Ch, Liaw HJ, SC Wang. The assessment of fire suppression capability for the ammonium dihydrogen phosphate dry powder of commercial fire extinguishers. Procedia Eng. 2014; 84: 485-490.
Huang X, Liu L, Zhou X. Experimental study on fires extinguishing performance of ammonia phosphate sub -nanometer powders. Fire Saf Sci. 2011; 4: 200 -205.
Trees D, Seshadri K. Experimental studies of flame extinction by sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) powders. Combust Sci Technol. 1997; 122(1/6): 215-230.
Dondur V. Hemijska kinetika. Beograd, Fakultet za fizičku hemiju; 1992.
Fudang S, Zhiming D, Xiaomin C, Linshuang Zh, Ye Y, Linming L. Experimental study on fires extinguishing properties of melamine phosphate powders. Procedia Eng. 2014; 84: 535-542.
Mihajlović S, Sekulić Ž, Radulović D, Jovanović V. Investigation the calcite hydrophobisation of different grain sizes. MME-Bor. 2016; 2: 31-40.
Mihajlović S, Sekulić Ž, Petrov M, Krstović P, Matejević B. Mikronizacija i oblaganje krečnjaka. Izgradnja. 2003; 319-321.
Mihajlović SR, Vučinić DD, Sekulić ŽT, Milićević SZ, Kolonja BM. Mechanism of stearic acid adsorption to calcite. Powder Technol. 2013; 245: 208-216.
Mihajlović S, Sekulić Ž, Radulović D, Stevanović D, Kašić V. Hidrofobizacija krečnjaka iz ležišta "Cancar" Aranđelovac upotrebom stearinske kiseline. Tehnika. 2015; 66(6): 943-946.
Mihajlović S, Sekulić Ž, Daković A, Vučinić D, Jovanović V, Stojanović J. Surface properties of natural calcite filler treated with stearic acid. Ceram-Silik. 2009; 53(4): 268-275.
Mihajlović SR, Daković AS, Sekulić ŽT, Ileš DA, Kragović MM. Površinska adsorpcija stearinske kiseline na prirodnom kalcitu. Hem Ind. 2009; 63(2): 101-106.
Đorđević N, Jovanić P. Influence of mechanical activation on electrical properties of cordierite ceramics. Sci Sinter. 2008; 40: 47-53.
Obradović N, Đorđević N, Filipović S, Nikolić N, Kosanović D, Mitrić M, Marković S, Pavlović V. Influence of mechanochemical activation on the sintering of cordierite ceramics in the presence of Bi2O3 as a functional additive. Powder Technol. 2012; 218: 157-161.
Obradović N, Đorđević N, Filipović S, Marković S, Kosanović D, Mitrić M, Pavlović V. Reaction kinetics of mechanically activated cordierite-based ceramics studied via DTA. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016; 124(2): 667–673.
Magdalinović N. Meljivost mineralnih sirovina. Beograd, Nauka; 1997.
SRPS ISO 7202:2019: Zaštita od požara-Sredstva za gašenje požara-Prah. 2019
Izveštaj o analizi, Sistem menadžmenta kvalitetom preduzeća "Centrohem" sertifikovan u skladu sa zahtevima ISO 9001:2008. Br. sertifikata: 75.100.9854-TUV Rheinland InterCert
Lobos ZJ. Dry chemical fire extinguisher composition. US Patent 3,214,372A, 1965
Xu Z, Guo X, Yan L, Kang W. Fire-extinguishing performance and mechanism of aqueous film-forming foam in diesel pool fire. Case Stud Therm Eng. 2020; 17: Article 100578.