Analiza novih oblika mernih blendi primenom računarske dinamike fluida
Main Article Content
Abstract
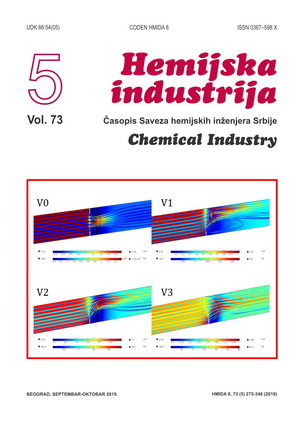
U mnogim granama tehnike javljaju se problemi merenja protoka fluida. Merne blende, zbog svojih mnogih prednosti predstavljaju najzastupljeniji instrument za merenje protoka fluida kroz cevovode. Sa druge strane njihova upotreba povećava troškove rada industrijskih postrojenja i cevovoda. U ovom radu dizajnirana su i ispitana tri nova oblika mernih blendi. Njihov cilj je bio ušteda energije, a samim tim i smanjenje troškova rada. Novi oblici mernih blendi, kao i jedna standardnog oblika koja je poslužila kao referentna, dizajnirani su u programskom paketu SolidWorks. Ušteda energije je postignuta dizajnom koji smanjuje otpor merne blende kao elementa cevovoda. Zatim su, prema predloženom algoritmu, dizajnirani oblici ispitani pomoću simulacije računarske dinamike fluida (RDF) u programskom paketu COMSOL Multiphysics i primenom tehnologije 3D štampanja, FDM postupkom (eng. Fused Deposition Modeling), izrađeni i ispitani u laboratorijskim uslovima. Rezultati laboratorijskih ispitivanja su prikazani uporedo sa rezultatima RDF simulacije. Dobijeni rezultati pokazuju znatan efekat uštede energije. Utvrđeno je da se pomoću RDF simulacije mogu dobiti podaci na osnovu kojih se može doneti odluka da li novi oblik merne blende treba korigovati ili ima smisla pristupiti laboratorijskom ispitivanju.
Article Details
Issue
Section
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors grant to the Publisher the following rights to the manuscript, including any supplemental material, and any parts, extracts or elements thereof:
- the right to reproduce and distribute the Manuscript in printed form, including print-on-demand;
- the right to produce prepublications, reprints, and special editions of the Manuscript;
- the right to translate the Manuscript into other languages;
- the right to reproduce the Manuscript using photomechanical or similar means including, but not limited to photocopy, and the right to distribute these reproductions;
- the right to reproduce and distribute the Manuscript electronically or optically on any and all data carriers or storage media – especially in machine readable/digitalized form on data carriers such as hard drive, CD-Rom, DVD, Blu-ray Disc (BD), Mini-Disk, data tape – and the right to reproduce and distribute the Article via these data carriers;
- the right to store the Manuscript in databases, including online databases, and the right of transmission of the Manuscript in all technical systems and modes;
- the right to make the Manuscript available to the public or to closed user groups on individual demand, for use on monitors or other readers (including e-books), and in printable form for the user, either via the internet, other online services, or via internal or external networks.
How to Cite
References
EN ISO 5167-1: Measurement of Fluid Flow by Means of Pressure Differential Devices Inserted in Circular Cross-Section Conduits Running Full. Part 1: General principles and requirements. 2003.
EN ISO 5167-2: Measurement of Fluid Flow by Means of Pressure Differential Devices Inserted in Circular Cross-Section Conduits Running Full. Part 2: Orifice plates. 2003.
Nicolleau FC. Return to axi-symmetry for pipe flows generated after a fractal orifice. Fluid Dyn. Res. 2013; 45:061402.
Gronych T, Jerab M, Peksa L, Wild J, Stanček F, Vičar M. Experimental study of gasflow through a multi-opening orifice. Vacuum 2012; 86:1759-1763.
Montagna F, Schena E, Massaroni C, Caciotti C, Presti DL, Silvestri S. Influence of the length of lead lines on the response of a variable orifice meter: analysis of sensitivity and settling time. In: IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Rome,2018, pp. 1-6.
Qiao M, Wei W, Huang W, Li J, Xue Y, Deng C. Flow patterns and hydrodynamic model for gas-liquid co-current downward flow through an orifice plate. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2019; 100:144-157.
Rydlewicz W, Rydlewicz M, Palczynski T. Experimental investigation of the influence of an orifice plate on the pressure pulsation amplitude in the pulsating flow in a straight pipe. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019; 117:634–652.
Mubarok MH, Zarrouk SJ, Cater JE. Two-phase flow measurement of geothermal fluid using orifice plate: Field testing and CFD validation, Renew. Energy 2019; 134:927–946.
Krassow H, Campabadal F, Lora-Tamayo E. The smart-orifice meter: a mini head meter for volume flow measurement. Flow Meas. Instrum. 1999; 10:109–115.
Perumal K, Ganesan R. Integration of numerical and physical experiments to enhance student learning experience. Comput Appl Eng Educ. 2018; 26:1930–1938.
Rudolf P, Kubina D, Kozak J, Hudec M, Pochyly F. Dynamics of the Cavitating Flow Downstream of the Orifice Plate. AIP Conference Proceedings 2017; 1889 (1):020033 8 pp.
Mancuso G. Experimental and numerical investigation on performance of a swirling jet reactor. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018; 49:241-248.
Wang LQ, Ma HH, Shen ZW. Effect of orifice plates on detonation propagation in stoichiometric hydrogen-oxygen mixture. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2018; 99:367-373.
Xu M Y, Zhang J P, Mi JC, Nathan GJ, Kaltp AM. PIV measurements of turbulent jets issuing from triangular and circular orifice plates. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron 2013; 56:11761186.
Kumar P, Wong M, Bing M. A CFD study of low pressure wet gas metering using slotted orifice meters. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2011; 22:33–42.
Moosa M, Hekmat MH. Numerical investigation of turbulence characteristics and upstream disturbance of flow through standard and multi-hole orifice flowmeters. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2019; 65:203–218.
Danesh M, Hassan AM. Estimation of Discharge Coefficient in Orifice Meter by Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation. In: International Conference on Pure and Applied Sciences. Koya University, Iraq, 2018 pp. 154-156.
Khan Z, Tafreshi R, Franchek M, Grigoriadis K. Numerical evaluation of pressure drop across orifices for different gas-liquid mixtures. In: Proceedings of the ASME 2018 Dynamic Systems and Control Conference DSCC2018. Atlanta, Georgia, USA, 2018, DSCC2018-9038, pp V003T30A007; 6 pages
Singh VK, Tharakan TJ. Numerical simulations for multi-hole orifice flow meter. Flow Meas.Instrum. 2015; 45:375-383.
Tukiman MM, Ghazali MNM, Sadikin A, Nasir NF, Nordin N, Sapit A, Razali MA. CFD simulation of flow through an orifice plate. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017; 243:012036.
Bramaramba V, Srinivasan S. Calculation of Coefficient of Discharge of Orifice Plate and Flow Nozzle Using CFD Analysis. IJMETMR. 2015; 2 (12):31-34.
Shaaban S. Optimization of orifice meters energy consumption. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014; 92:1005-1015.
S. Manish Shah, B. Jyeshtharaj Joshi, S. Avtar Kalsi, C.S.R. Prasad, S. Daya Shukla, Analysis of flow through an orifice meter: CFD simulation, Chem. Eng. Sci. 71 (2012) 300–309.
He D, Chen S, Bai B. Experiment and Numerical Simulation on Gas-Liquid Annular Flow through a Cone Sensor. Sensors. 2018; 18(9):2923.
Mubarok, Mohamad & Zarrouk, Sadiq & Cater, John. (). Numerical and analytical modeling of pressure drop through a geothermal two-phase orifice plate. In: Proceedings 40th New Zealand Geothermal Workshop, Taupo, New Zealand, 2018.
Kuzmin D, Mierka O, Turek S. On the implementation of the k – ε turbulence model in incompressible flowsolvers based on a finite element discretization. Int. J. Comp. Sci. Math. 2007; 2/3/4:193–206.