EFFECT OF STORAGE PROCESS ON NUTRITIVE PROPERTIES OF PRETERM HUMAN MILK
Scientific paper
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.2298/CICEQ220117021LKeywords:
preterm human milk, pasteurization, freeze storageAbstract
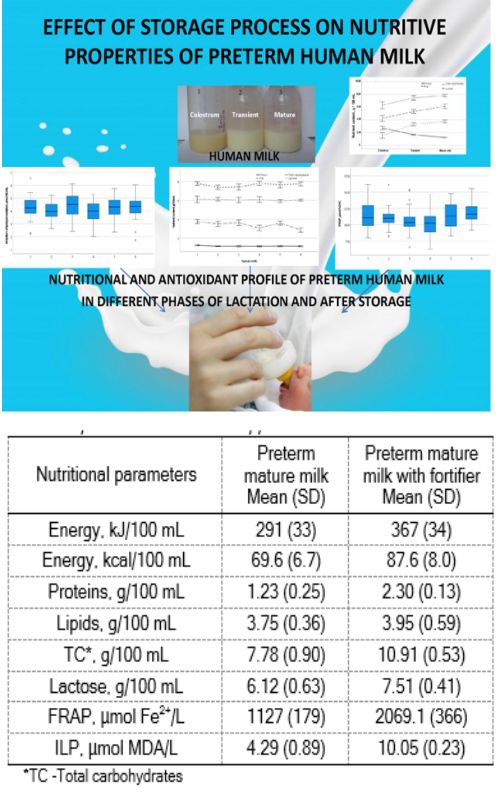
Freeze storage and pasteurization of human milk are common treatments in milk banks. However, thermal treatment changes milk quality for preterm infants’ nutrition. Therefore, this paper aimed to examine preterm human milk's nutritional profile and antioxidant potential after storage, pasteurization, and after supplementation with a fortifier. The effects of storage processes were estimated on the mature preterm milk of 30 breastfeeding women. Total proteins, lipids, and lactose were determined after thermal processing and supplementing mature preterm milk with a fortifier. The ferric-reducing antioxidant potential method and lipid peroxidation inhibition assay determined the antioxidant capacity. Protein concentration decreased after frozen storage and pasteurization (p<0.05). Pasteurization further reduced the lipid concentration after freezing. The ferric-reducing antioxidant potential decreased after thermal treatments (p<0.05). Supplementing mature milk with a fortifier increased the concentration of proteins, lipids, and lactose. Our findings demonstrated that storage and pasteurization processes affect preterm human milk's basic nutritional composition and antioxidant capacity. To ensure adequate nutrition for preterm infants with preterm human milk, supplementation, especially with high concentrations of proteins and lipids, is necessary after thermal treatments.
References
World Health Organization. Guidelines on optimal feeding of low birth-weight infants in low- and middle-income countries. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/documents/infant_feeding_low_bw/en/ ⦋accessed 21 April 2021⦌.
H.G. Kanmaz, B. Mutlu, F.E. Canpolat, O. Erdeve, S.S. Oguz, N. Uras, U. Dilmen, J. Hum. Lactation 29 (2013) 400—405. https://doi.org/10.1177/0890334412459.
B. Lonnerdal, Nutrition 16 (2000) 509—511. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0899-9007(00)00363-4.
M. A. Underwood, Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 60(1) (2013) 189—207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcl.2012.09.008.
J. Kim, S. Unger, Paediatr. Child Health 15(9) (2010) 595—598. https://doi.org/10.1093/pch/15.9.595.
C. Pound, S. Unger, B. Blair, Paediatr. Child Health 25(8) (2020) 549—550. https://doi.org/10.1093/pch/pxaa118.
C. Hanson, E. Lyden, J. Furtado, M. Van Ormer, A. Anderson-Berry, Nutrients 8 (2016) 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8110681.
Y. Ozsurekci, K. Aykac, Oxid. Med. Cell. Longevity (2016) ID 2768365. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2768365.
C. Matos, M. Ribeiro, A. Guerra, J. Appl. Biomed. 13 (2015) 169—180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jab.2015.04.003.
D. Huang, B. Ou, RL Prior, J. Agric. Food Chem. 23 (2005) 1841—1856. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf030723c.
I.F. Benzie, J.J. Strain, Methods Enzymol. 299 (1999) 15—27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(99)99005-5.
K. Jomova, M. Valko, Toxicology 283 (2011) 65—87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2011.03.001.
C. Agostini, G. Buonocore, V.P. Carnielli, M. De Curtis, D. Darmaun, T. Decsi, M. Domellöf, N.D. Embleton, et al., J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 50 (2010) 85—91. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181adaee0.
A. Choi, G. Fusch, N. Rohow, C. Fusch, Plos One 11(2) (2016) e0148941. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0148941.
S. Arslanoglu, G.E. Moro, E.E. Ziegler, J. Perinat. Med. 38(3) (2010) 233—238. https://doi.org/10.1515/jpm.2010.073.
N. Lugonja, D. Stankovic, B. Milicic, S. Spasic, V. Marinkovic, M.M. Vrvic, Food Chem. 240 (2018) 567—572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.07.164.
N. Kamizakea, M. Gonçalves, T.B.V. Cássia, C. Zaia, D. Zaia, J. Food. Compost. Anal. 16 (2003) 507—516. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0889-1575(03)00004-8.
EN ISO 8262-1|IDF 124-1: Milk products and milk-based foods — Determination of fat content by the Weibull-Berntrop gravimetric method (Reference method) — Part 1: Infant foods (2005). https://www.iso.org/standard/42070.html.
H.O. Beutler, in Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, Bergmeyer, H. U. Ed., VCH Publishers (UK.) Ltd, Cambridge, UK, (1988), p. 104. ISBN 978-0-12-091302-2.
FAO, in Food Energy – Methods of Analysis and Conversion Factors; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, (2003), p.77. ISBN 92-5-105014-7.
I.F. Benzie, J.J. Strain, Anal. Biochem. 239 (1996) 70—76. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1996.0292.
R.D. Janero, Free Rad. Biol. Med. 9 (1990) 515—540. https://doi.org/10.1016/0891-5849(90)90131-2.
N. García-Lara, D. Vieco, D.J. Cruz-Bértolo, D. Lora, N. Ureta-Velasco, C. Pallás-Alonso, J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 57(3) (2013) 377—382. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0b013e31829d4f82.
O. Ballard, A.L. Morrow, Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 60 (2013) 49—74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcl.2012.10.002.
C.A. Butts, D.I. Hedderley, T.D. Herath, G. Paturi, S. Glyn-Jones, F. Wiens, B. Stahl, P. Gopal, Nutrients 10(9) (2018) 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091231.
L. Lamport, C. Hartman, C. Codipilly, B. Weinberger, R. Schanler, J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 43 (2018) 809—814. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpen.1470.
A.A. Vieira, F.V. Soares, H.P. Pimenta, D. Abranches , E. Moreira, Early Hum. Dev. 87(8) (2011) 577—580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2011.04.016.
V. Marinković, M. Ranković-Janevski, S. Spasić, A. Nikolić-Kokić, N. Lugonja, D. Djurović, S. Miletić, M. Vrvić, I. Spasojevic, J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 62 (2016) 901—906. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000001090.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Nikoleta Lugonja, Vesna Marinković, Biljana Miličić, Jelena Avdalović, Miroslav Vrvić, Snežana Spasić

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors grant to the Publisher the following rights to the manuscript, including any supplemental material, and any parts, extracts or elements thereof:
- the right to reproduce and distribute the Manuscript in printed form, including print-on-demand;
- the right to produce prepublications, reprints, and special editions of the Manuscript;
- the right to translate the Manuscript into other languages;
- the right to reproduce the Manuscript using photomechanical or similar means including, but not limited to photocopy, and the right to distribute these reproductions;
- the right to reproduce and distribute the Manuscript electronically or optically on any and all data carriers or storage media – especially in machine readable/digitalized form on data carriers such as hard drive, CD-Rom, DVD, Blu-ray Disc (BD), Mini-Disk, data tape – and the right to reproduce and distribute the Article via these data carriers;
- the right to store the Manuscript in databases, including online databases, and the right of transmission of the Manuscript in all technical systems and modes;
- the right to make the Manuscript available to the public or to closed user groups on individual demand, for use on monitors or other readers (including e-books), and in printable form for the user, either via the internet, other online services, or via internal or external networks.