SIMULATION STUDY OF CITRIC ACID EFFECTS ON PYROLYSIS OF HYDROCHLORIC ACID PICKLING WASTE LIQUOR
Scientific paper
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.2298/CICEQ211003013CKeywords:
pyrolysis, citric acid, Fe2O3, Fe3O4, numerical simulationAbstract
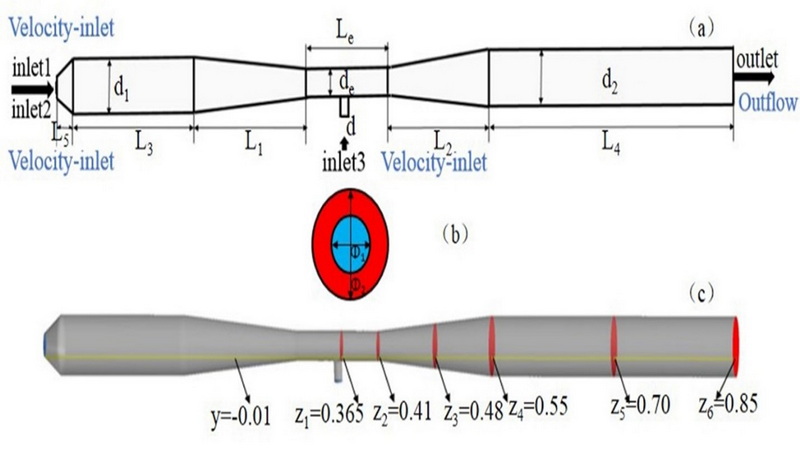
During pyrolysis of hydrochloric acid pickling waste liquid in a Venturi reactor from iron and steel enterprises, the reaction products agglomerated and hindered product recovery. Addition of citric acid to materials at the inlet improved product distribution. In this paper, a numerical simulation of the combustion, phase change, and gas-solid chemistry involved in a citric acid-added pickling waste liquid was conducted. These results showed that citric acid added to the inlet resulted in a peak concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the back half of the Venturi throat, and some ferric oxide (Fe2O3) underwent a secondary reaction to afford ferroferric oxide (Fe3O4). As the addition of citric acid increased, the flow of Fe2O3 at the outlet first increased and then decreased, while the flow rate of Fe3O4 first decreased and then increased. When the ratio of citric acid was 7%, the flow rate of Fe2O3 was the smallest, and the flow rate of Fe3O4 was the largest.
References
J. Peng, Y. Zhu, D.F. Zhang, Inor. Chem. Ind. 07 (2019) 81—84.
Y.T. Hong, L. Qiao, X.H. Liu, Mod. Chem. Ind. 01 (2005) 48—50.
A.J. Sushilkumar, B Roberta, L.M. Daniele, F. Daniela, E. Christian, Pigm. Resin. Tech. 04 (2014) 219—227. https://doi.org/10.1108/PRT-07-2013-0057
M. A. Ali, M. M. Uddin, M. N. I. Khan, F.U.Z. Chowdhury, S.M. Hoque, S.I. Liba, Chin. Phy. B. 07 (2017) 377—343. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/26/7/077501
X. Han, L.L. Wang, L. Wang, X.D. Wang, D.Q. Zhao, J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 07 (2020) 1097—1106. https://doi.org/10.14062/j.issn.0454-5648.2020.07.20190682
Y. Aylin, V.B. Derman, A. Riza, A.A. Ozgur, A. K. Mine, E. Ugur, M. Carl, H.R.L. Appl. Surf. Sci. 521 (2020) 146332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146332.
S. Yousefinejad, H. Rasti M. Hajebi, M. Kowsari, S. Sadravi, F. Honarasa, Sens. Actuators, B 247 (2017) 691-696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.02.145.
C.X. Cui, Coal. Chem. Ind, 11 (2010), 37—38.
Y.T. Liu, F.Z. Liu, W. Du, G.M. Lu, J.G. Yu, J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 6 (2018) 1010-1015.
AlShammari A. S., Halim M.M., Yam F.K., K. N. H. Mohd, Mate. Sci. Semi. Proc, 116 (2020) 1—6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2020.105140
A. Moumen, B. Hartiti, E. Comini, Z.El Khalidi, H.M.M.M. Arachchige, S. Fadili, P. Thevenin, Supe. micr, 127 (2019) 2—10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2018.06.061
Lv, C., Zhang, T. A., and Dou, Z. H., Rare Metals, 12 (2019) 1160—1168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01337-9
C. Lv, T.A. Zhang, Z.H. Dou, Q.Y. Zhao, J. Mate, 5 (2019) 1660—1666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03397-9
C. Lv, J. Mate, 12 (2019) 4944—4949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01337-9
G.S. Yang, X. Bian, L.X. Cui, B. Xie, Y.L. Yao, W.Y. Wu. Chin. Rare. Earths, 01 (2017) 72—78. https://doi.org/10.16533/J.CNKI.15-1099/TF.201701013
D.L. Ye, Beijing: Metallurgical industry press, (1981) 250—257. (in Chinese).
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors grant to the Publisher the following rights to the manuscript, including any supplemental material, and any parts, extracts or elements thereof:
- the right to reproduce and distribute the Manuscript in printed form, including print-on-demand;
- the right to produce prepublications, reprints, and special editions of the Manuscript;
- the right to translate the Manuscript into other languages;
- the right to reproduce the Manuscript using photomechanical or similar means including, but not limited to photocopy, and the right to distribute these reproductions;
- the right to reproduce and distribute the Manuscript electronically or optically on any and all data carriers or storage media – especially in machine readable/digitalized form on data carriers such as hard drive, CD-Rom, DVD, Blu-ray Disc (BD), Mini-Disk, data tape – and the right to reproduce and distribute the Article via these data carriers;
- the right to store the Manuscript in databases, including online databases, and the right of transmission of the Manuscript in all technical systems and modes;
- the right to make the Manuscript available to the public or to closed user groups on individual demand, for use on monitors or other readers (including e-books), and in printable form for the user, either via the internet, other online services, or via internal or external networks.